4.7 KiB
Table of Contents
Smon
Smon (Simple Monitoring) is a small and easy to maintain single user monitoring system.
It is developed for the developer's personal need for monitoring a small number of datapoints and get notifications,
without having to maintain a huge system like Zabbix.
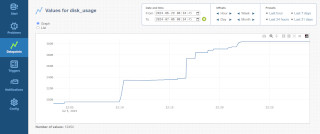
It is also possible to troubleshoot with historial data and graphs.
There is no concept of users or passwords.
If a requirement, authentiation and authorization can be handled by a HTTP reverse proxy.
All data is sent to the system via an HTTP request to /entry/datapoint_name.
Smon can't poll data.
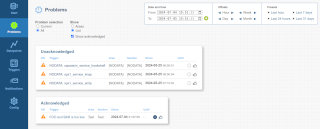
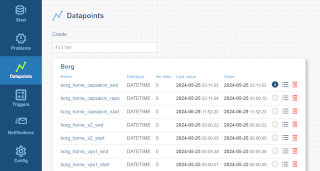
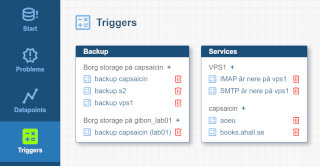
Screenshots
| Problems | Datapoints | Graphs | Triggers |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Quick start
- Create an empty database (smon only supports PostgreSQL).
- Create the configuration file (default ~/.config/smon.yaml).
- Run ./smon (will create the database schema).
Configuration
network:
address: "[::]"
port: 9000
websocket:
domains:
- localhost
- smon.example.com
database:
host: localhost
port: 5432
name: smon
username: smon
password: you_wish
application:
logfile: /var/log/smon.log
nodata_interval: 60
Sending data to datapoints
curl -d 200 http://localhost:9000/entry/datapoint_name
Use date '+%FT%T%z' to get a value from systems in correct format.
Concepts
Core concepts in Smon are:
- datapoints.
- triggers.
- problems.
- notifications.
- areas.
Datapoints
A datapoint has a unique name. Recommended is to use only a-z, A-Z, 0-9, dots, dashes and underscores for easier handling in URLs and trigger conditions.
There are three data types:
- INT.
- STRING.
- DATETIME.
INT accepts values like -100, 0, 137 and 29561298561 and is stored in the int8 postgresql type.
STRING is text data and stored by an unlimited varchar.
DATETIME is a date with time and timezone in the format of 2006-01-02T15:04:05+02:00 or 2006-01-02T15:04:05+0200. Stored in a field of timestamptz.
Recommended is to provide from where (machine, system or script location...) the data is being pushed to Smon in the comment field.
Triggers
Triggers have datapoints the expression is being able to use.
Expressions are written with the Expr language. See the language reference for available functions and syntax.
The trigger is evaluating the expression when data is entered through the /entry/datapoint_name URL and a problem is issued when the expression returns true.
Problems
One or more datapoints that trips a trigger issues a problem.
Problems are archived in the database and can be looked up historically.
A page of current problems is available to see the current problem state, either as a list or categorised.
Problems can be acknowledged if they are known problems that will not be currently fixed.
Notifications
Smon has a couple of notification services (currently NTFY and script).
Services are added with a prio. The service with the lowest prio is tried first.
If sending through the service fails, the next service is tried and so on until one succeeds.
What is sent isn't configurable (for now). What is sent is:
- PROBLEM (when a problem is created) or OK (when a trigger evaluates to false).
- Trigger name
NTFY
An URL is provided to the topic which should receive the notifications.
Script
The script service is defined with a filename.
The script is called with three parameters:
- Problem ID
- Acknowledge URL
- Message
Areas
Go to the Config icon to add areas. These are available to categorize triggers and problems for easier troubleshooting.
Each area has sections to further group problems and triggers.
Development
A couple of small notes on development.
Theming
- Add theme to select tag in
/views/pages/configuration.gotmpl. - Create
/static/less/theme-<theme-name>.less. - Create
/static/less/<theme-name>.less. - Copy a theme directory under
/static/images/to the new name.